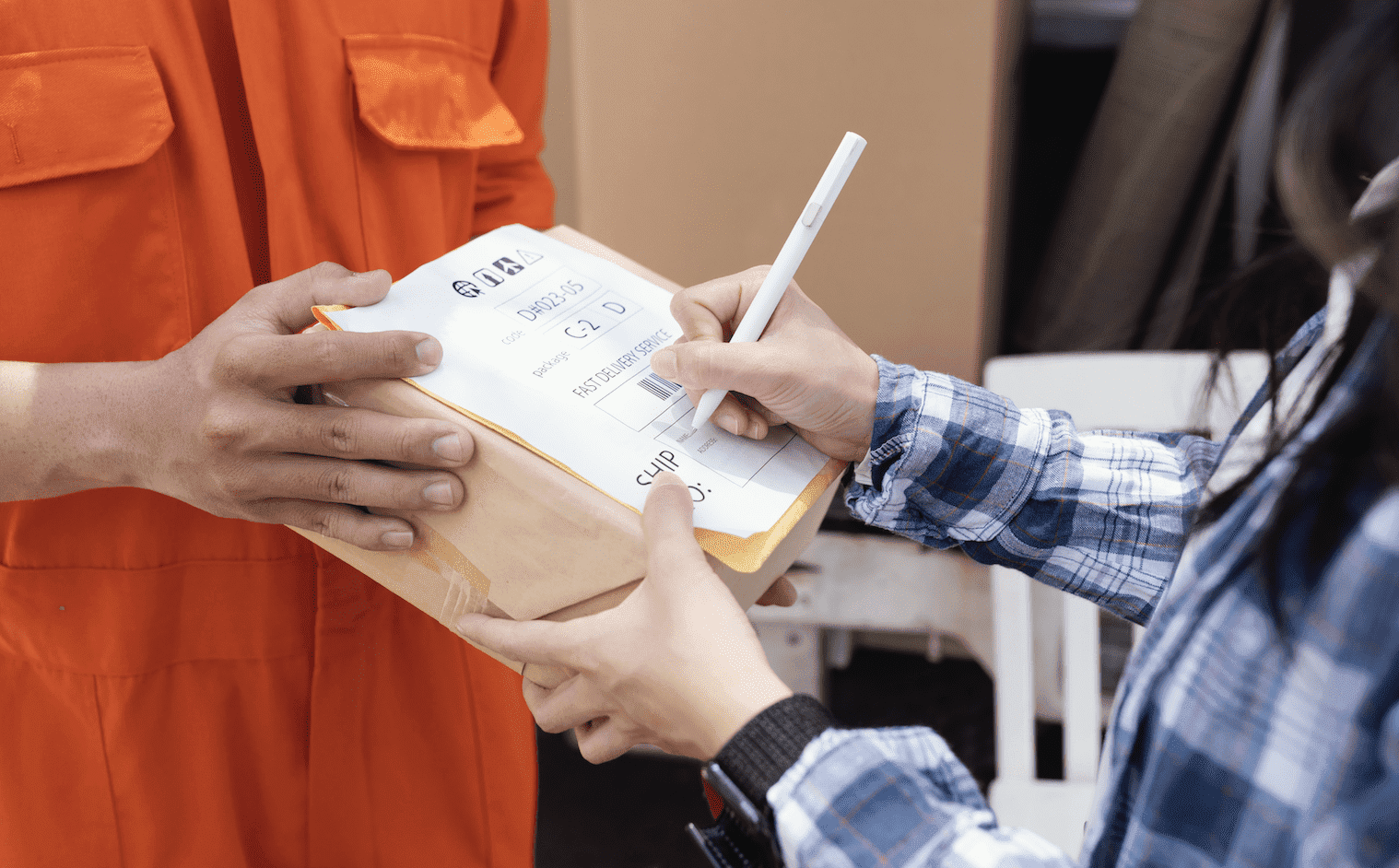
How to Effectively Measure Delivery Performance?
The transportation cost alone can consume around 10% of the total revenue. The profitability of the business is significantly impacted by this considerable percentage. Therefore, evaluating delivery performance in order to maximize the efficiency of the fleet is thought to be an essential aspect for 3PLs or suppliers. Besides ensuring effective fleet operations and timely deliveries, measuring delivery performance also helps control costs and evaluate business operations more effectively.
Delivery performance is basically the efficiency of a business in meeting order requirements, providing products/services to customers. Businesses should create appropriate Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure in order to have standards for evaluating and rating the performance of each driver. To optimize the operation of any fleet, KPIs for assessing delivery performance must be integrated effectively.
Below are some suggested criteria for measuring delivery performance:
- The number of completed deliveries: This metric measures the total number of completed deliveries within a specific timeframe, such as a month, quarter, or year. It is a fundamental indicator that influences other performance values and offers information about the delivery operations’ overall effectiveness.
- On-Time Delivery: This statistic calculates the percentage of deliveries that are completed on time as per the customer’s requirements, with the others are considered late deliveries.
- Transit Time to Distance: This metric provides an overview of the time taken by drivers or delivery personnel during transportation from the pickup location to the delivery destination. Measuring this index helps assess the speed of drivers and the efficiency of delivery routes.
- Vehicle Capacity vs. Available Capacity: Comparing the actual transportation capacity of delivery vehicles to the total capacity of the business. It helps identify the number of idle vehicles and assess the efficiency of vehicle utilization.
- Average Time per Delivery: Calculating the average time required to complete a single delivery.
- Average Delivery Cost: This KPI calculates the average cost of delivery based on factors such as distance, products, and types of vehicles.
- Route Compliance: Designing optimized delivery routes for delivery fleets ensures cost savings and efficiency. Therefore, monitoring driver compliance with the specified routes is essential.
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) or Application Programming Interface (API) Invoicing: Generating an EDI or API invoice incurs lower costs by 81% compared to manual invoices and reduces processing time by 77%. If a business is using TMS (Transportation Management Systems) with integrated electronic invoicing for drivers, successful implementation of EDI/ADI can be considered as part of the fleet’s KPI.
In conclusion, in today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, measuring delivery performance is a crucial practice for logistics and carrier companies. Enterprises may optimize their delivery operations, assure on-time deliveries, make informed choices to improve performance based on KPI analysis, raise customer satisfaction, and maintain their competitive edge by using and monitoring important KPIs.
*Source: optimoroute.com