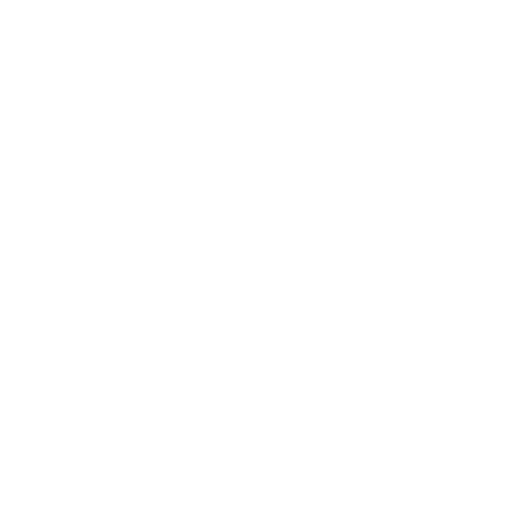
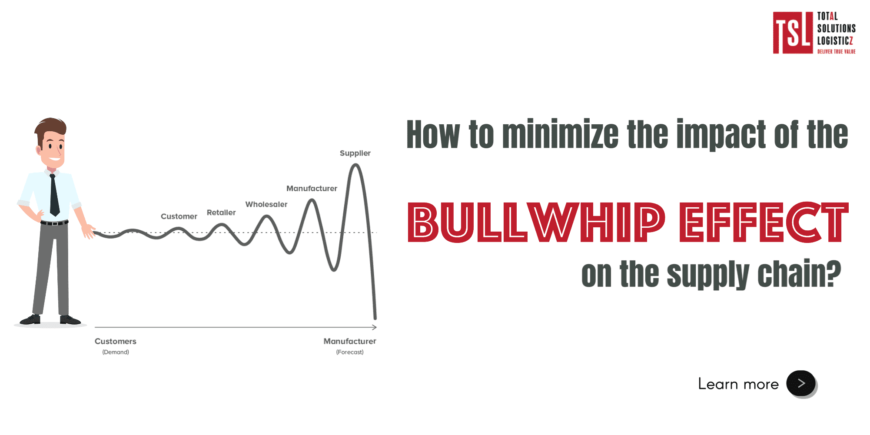
How to minimize the impact of the Bullwhip effect on the supply chain?
As the production and distribution enterprises move further away from the end customer, the signal of demand arising in the market will be at greater risk of deviation. At some point, this deviation can be up to 3 to 5 times the original demand. And when demand is returned incorrectly, the supply chain will be negatively impacted, the cause of this problem is the Bullwhip effect…
What is the Bullwhip Effect?
The Bullwhip effect is a phenomenon where the market demand for a product downstream is altered and leads to fluctuations in vertical linkages across the supply chain. It entails excess inventory, affects pricing policy and creates an inaccurate reflection in market demand.
Imagine a person having a long whip in his hand, and if he gives a little nudge to the whip at the handle, it creates little movements in the parts closest to the handle, but parts further away would move more in an increasing fashion.
Similarly, in the supply chain world, the end customers have the whip handle and they create a little movement in the demand which travels up the supply chain in an increasing fashion. As we move away from the customer, we can see bigger movements.
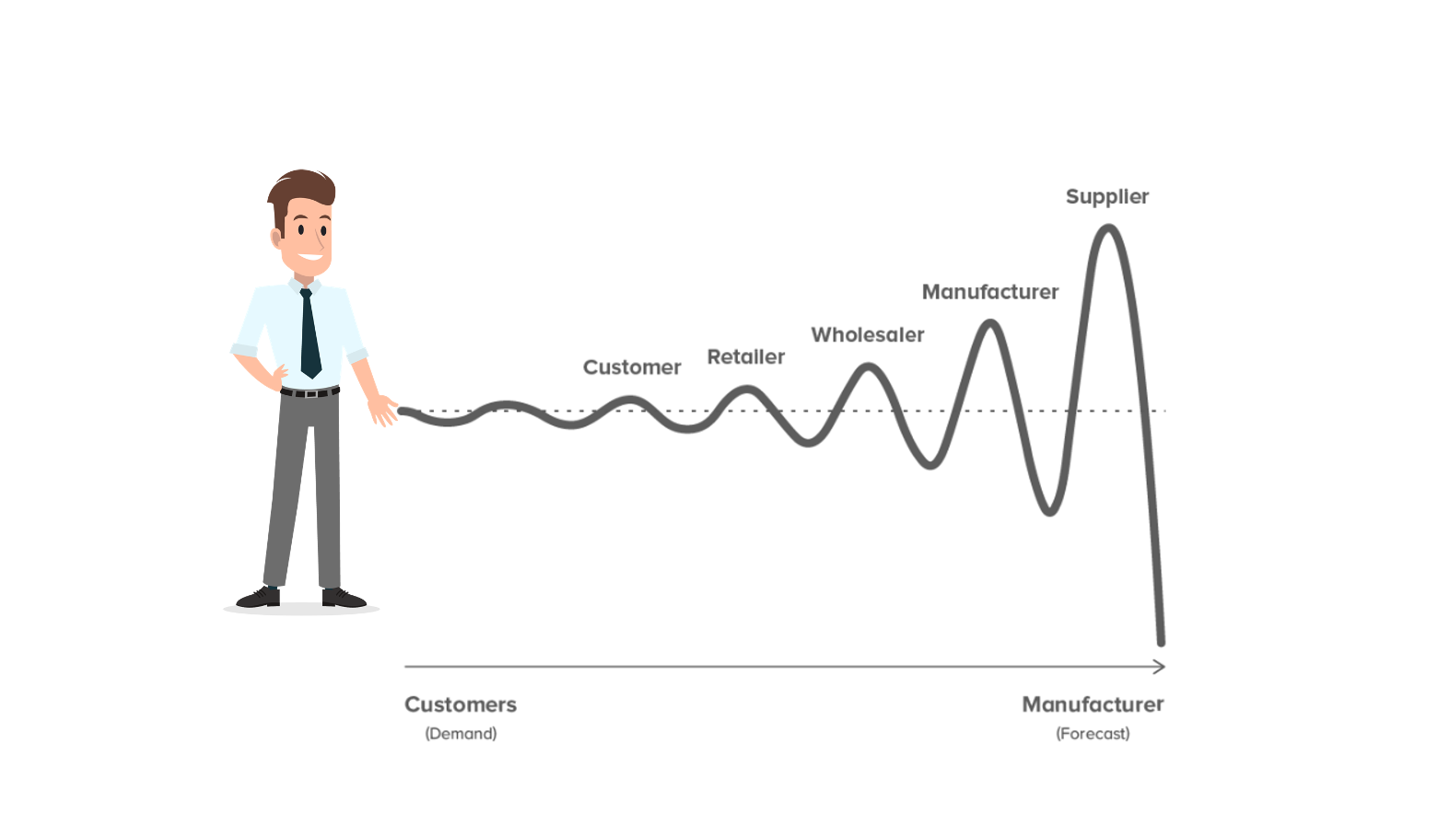 On average, there are six to seven inventory points between the end customer and raw material supplier. Everyone tries to protect themselves from stock-out situations and missed customer orders, by keeping extra inventory to hedge against variability in the supply chain. Hence, huge buffers of inventories up to six months can exist between the end customer and raw material supplier. This bullwhip effect ultimately causes the upstream manufacturers to have increased uncertainty which results in lower forecast accuracies leading to higher inventories.
On average, there are six to seven inventory points between the end customer and raw material supplier. Everyone tries to protect themselves from stock-out situations and missed customer orders, by keeping extra inventory to hedge against variability in the supply chain. Hence, huge buffers of inventories up to six months can exist between the end customer and raw material supplier. This bullwhip effect ultimately causes the upstream manufacturers to have increased uncertainty which results in lower forecast accuracies leading to higher inventories.
Causes of the Bullwhip Effect?
The core reason behind demand distortion is believed to be the imperfection of information received between actors in the supply chain, through four main causes:
- Demand forecast updating is done individually by all members of a supply chain. Each member updates its own demand forecast based on orders received from its “downstream” customer. The more members in the chain, the less these forecast updates reflect actual end-customer demand.
- Order batching occurs when each member takes order quantities it receives from its downstream customer and rounds up or down to suit production constraints such as equipment setup times or truckload quantities. The more members who conduct such rounding of order quantities, the more distortion occurs of the original quantities that were demanded.
- Price fluctuations due to inflationary factors, quantity discounts, or sales tend to encourage customers to buy larger quantities than they require. This behavior tends to add variability to quantities ordered and uncertainty to forecasts.
- Rationing and gaming is when a seller attempts to limit order quantities by delivering only a percentage of the order placed by the buyer. The buyer, knowing that the seller is delivering only a fraction of the order placed, attempts to “game” the system by making an upward adjustment to the order quantity. Rationing and gaming create distortions in the ordering information that is being received by the supply chain.
How the Bullwhip Effect Impacts the Supply Chain?
The Bullwhip effect causes significant impacts on the performance of supply chains and businesses.
- Increasing costs: The Bullwhip effect will make the excess product volume too large, leading to too much inventory, a sharp increase in storage and handling costs. In addition, the goods also face damage due to being in the warehouse for too long.
- Increased labor: You need to pay employees to handle, sort, and sell additional items on-hand. Similarly, if a seller runs out of stock, salespeople may need to work harder to locate alternatives or arrange for deliveries later. These labor demands can add up.
- Unmet customer expectations: Running out of a product can cause problems for your reputation and profits. Whether you’re trying to meet the demands of consumers or other supply chain members, being unable to provide products can upset your customers, make you look less reliable, and cause some of them to look for new partners or brands.
- Stagnation in production and circulation: Excess production will make it difficult for all subjects to consume, ensure quality, delay the circulation and production process, investment capital cannot be rotated.
- Reduced competitive advantage: Stemming from the bullwhip effect that causes costs to increase, businesses must increase product prices to compensate, thereby reducing their competitive advantage in price in the market.
How to minimize the impact of the Bullwhip effect on the supply chain?
Optimizing supply chain actors
Reducing the number of suppliers as well as reducing intermediaries in the supply chain can help limit the impact of the Bullwhip effect. Because the simpler a supply chain is, the easier it is to communicate information between entities and will reduce information magnification.
Optimize the minimum order quantity and offer stable pricing
Certain products have high minimum order quantity for end customers resulting in overall high gaps between subsequent orders. Lowering the minimum order quantity to an optimal level will help provide create smoother order patterns. Stable pricing throughout the year instead of frequent promotional offers and discounts may also create stable and predictable demand.
Improve the raw material planning process
Purchase managers generally tend to order in advance and keep high buffers of raw material to avoid disruption in production. Raw material planning needs to be directly linked to the production plan. Production plan needs to be released sufficiently in advance to respect the general purchasing lead times. Consolidation to a smaller vendor base from a larger vendor base, for similar raw material, will improve the flexibility and reliability of the supplies. This, in turn, will result in lower raw material inventories.
Improve the inventory planning process
Inventory planning is a careful mix of historical trends for seasonal demand, forward-looking demand, new product launches and discontinuation of older products. Safety stock settings and min-max stock range of each inventory point need to be reviewed and periodically adjusted. Inventories lying in the entire network need to be balanced based on regional demands. Regular reporting and early warning system need to be implemented for major deviations from the set inventory norms.
Use Warehouse Inventory Management Software
Proper inventory and order management go a long way to avoiding problems with the bullwhip effect. This is best done using software that can track inventory levels, product flows, and orders in real-time. They give you actionable data and provide detailed insight into your ability to meet demand. Even better, they can help you set par level, calculate optimal reorder points, and avoid wasting money on storing excess inventory.
*Source: Synthesis